Network Transport Configuration#
The software supports two different types of transports per default. REST and SOAP. Below you will find the differences in the configuration.
Note
Other transports may be delivered with specific add-ons and customizations. Please refer to the documentation for configuration of these transports as they will differ.
Any single webservice ma have one requester and one invoker transport configuration. These need not use the same protocol.
SOAP#
Read more about SOAP online at Wikipedia.
SOAP Provider Transport#
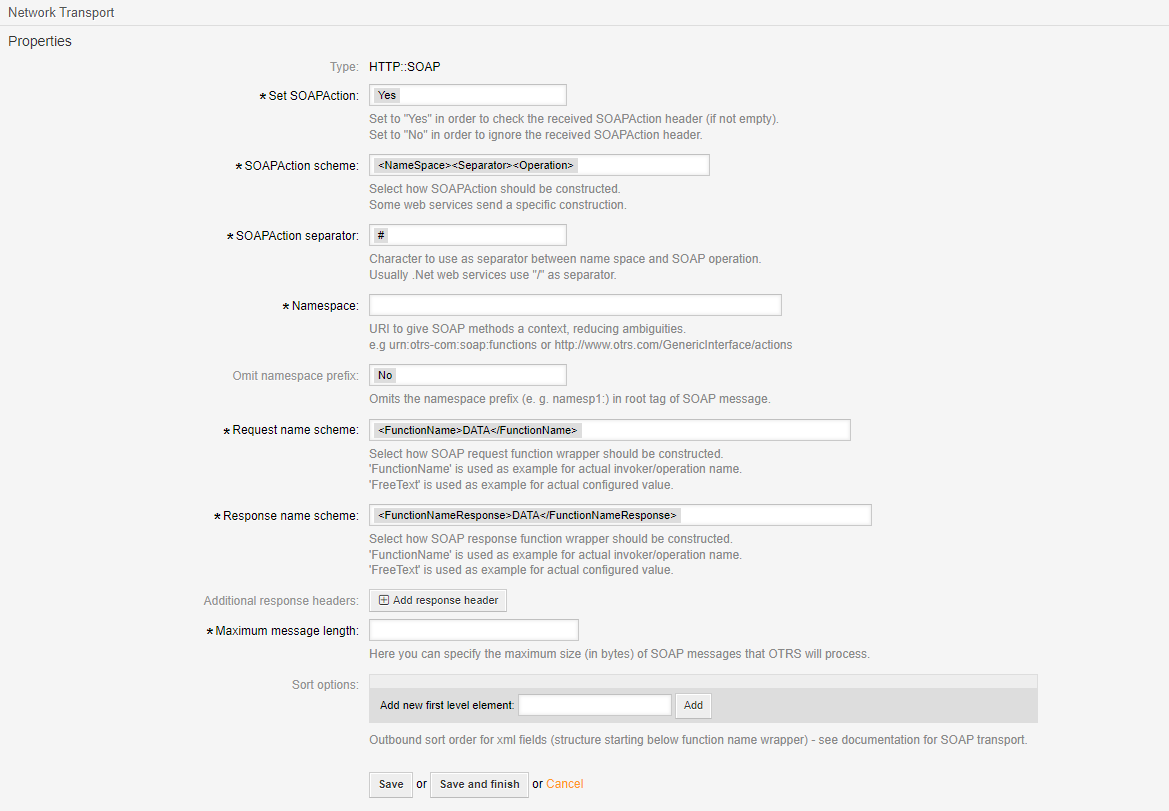
- Set SOAPAction
Check or ignore the SOAPAction header (if not empty).
- SOAPAction scheme:
Select how SOAPAction should be constructed. Some web services send a specific construction.
- SOAPAction separator
Character to use as separator between name space and SOAP operation. Usually .Net web services use “/” as separator.
- Namespace:
URI to give SOAP methods a context, reducing ambiguities.
Note
An exapmle urn:otrs-com:soap:functions or http://www.otrs.com/GenericInterface/actions
- Omit namespace prefix
Omits the namespace prefix (e. g. namesp1:) in root tag of SOAP message.
- Request name scheme
Select how SOAP request function wrapper should be constructed.
- Response name scheme:
Select how SOAP response function wrapper should be constructed.
- Additional response headers
Add response header.
- Maximum message length
Here you can specify the maximum size (in bytes) of SOAP messages that Znuny will process.
- Sort options
Outbound sort order for xml fields (structure starting below function name wrapper) - see documentation for SOAP transport.
SOAP Requester Transport#
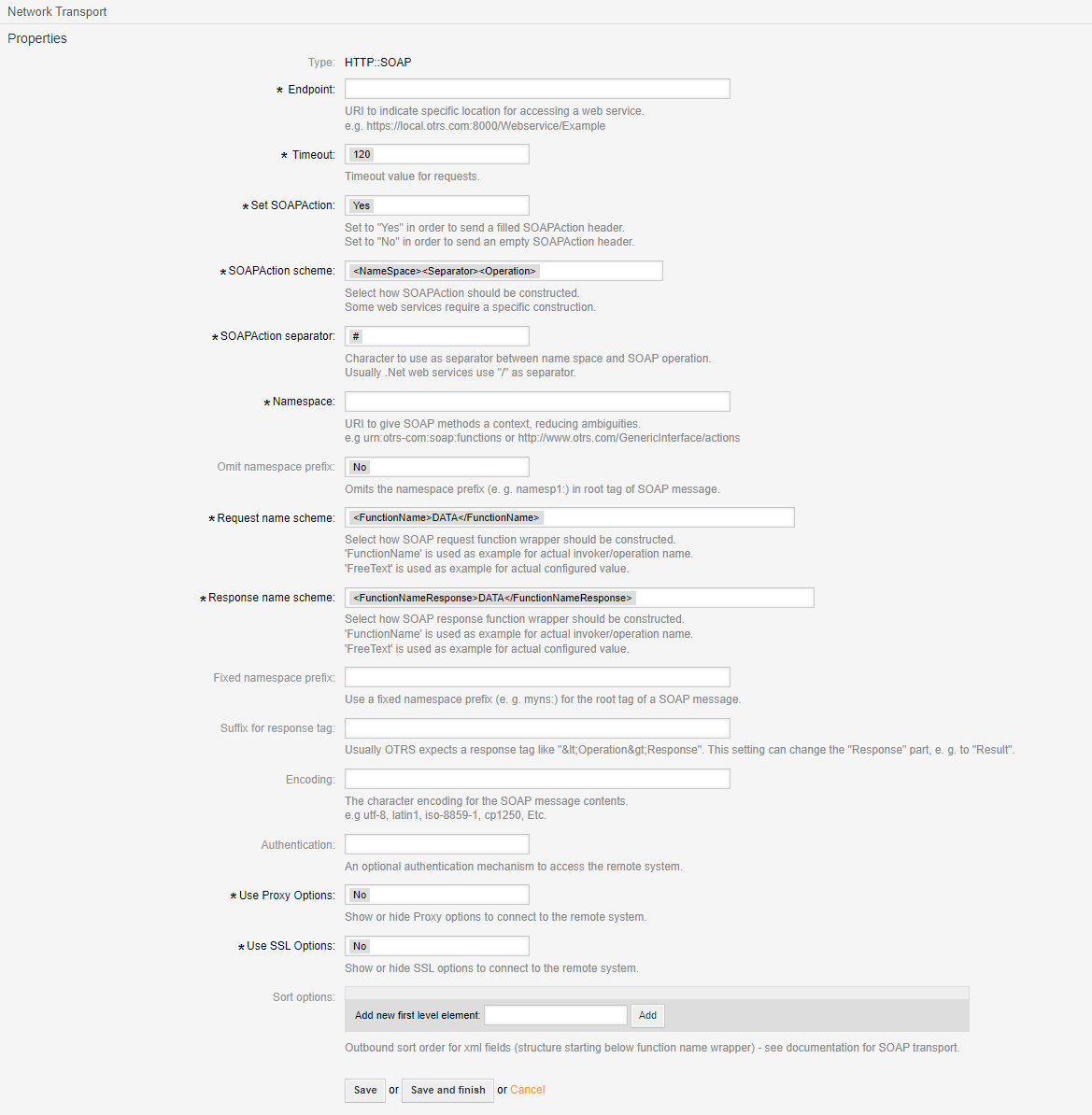
- Name
The name will be the SOAP Action called.
- Description
Description for the administrator of what the invoker does.
- Invoker backend
This invoker backend module will be called to prepare the data to be sent to the remote system, and to process its response data.
- Mapping for outgoing request data
The data from the invoker of Znuny will be processed by this mapping, to transform it to the kind of data the remote system expects.
- Mapping for incoming response data
The response data will be processed by this mapping, to transform it to the kind of data the invoker of Znuny expects.
- Event Triggers
The event to trigger the invoker.
- Add Event Trigger
Add the event to trigger the request by selecting the event object and event name and click on the “+” button.
Important
Asynchronous event triggers are handled by the Znuny Scheduler Daemon in background (recommended). Synchronous event triggers would be processed directly during the web request.
- Add all attachments
Add all attachments to invoker payload.
REST#
Read more about REST online at Wikipedia
REST Provider Transport#
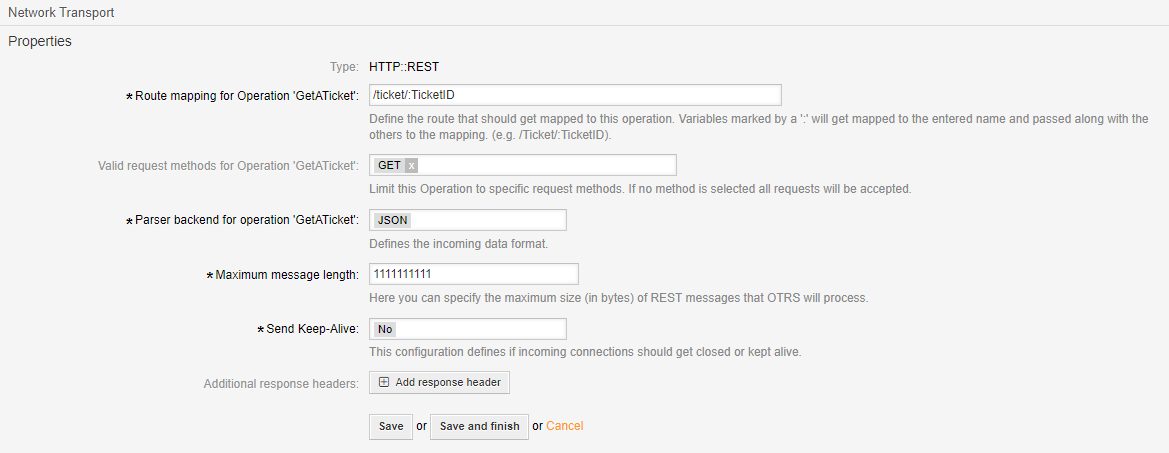
- Route mapping for Operation ‘GetATicket’:
In this example we use /ticket/:TicketID
Note
This setting first appear when you’ve configured an operation for use.
Define the route that should get mapped to this operation. Variables marked by a ‘:’ will get mapped to the entered name and passed along with the others to the mapping. (e.g. /Ticket/:TicketID).
Important
If you rename an operation, this setting will be lost and you must configure it again for the new name.
- Valid request methods for Operation ‘GetATicket’
Limit this Operation to specific request methods. If no method is selected all requests will be accepted.
Note
This setting first appear when you’ve configured an operation for use.
- Parser backend for operation ‘GetATicket’
Defines the incoming data format.
Note
This setting first appear when you’ve configured an operation for use.
- Maximum message length
Here you can specify the maximum size (in bytes) of REST messages that Znuny will process.
- Send Keep-Alive
This configuration defines if incoming connections should get closed or kept alive.
- Additional request headers
Add request header(s)
REST Requester Transport#
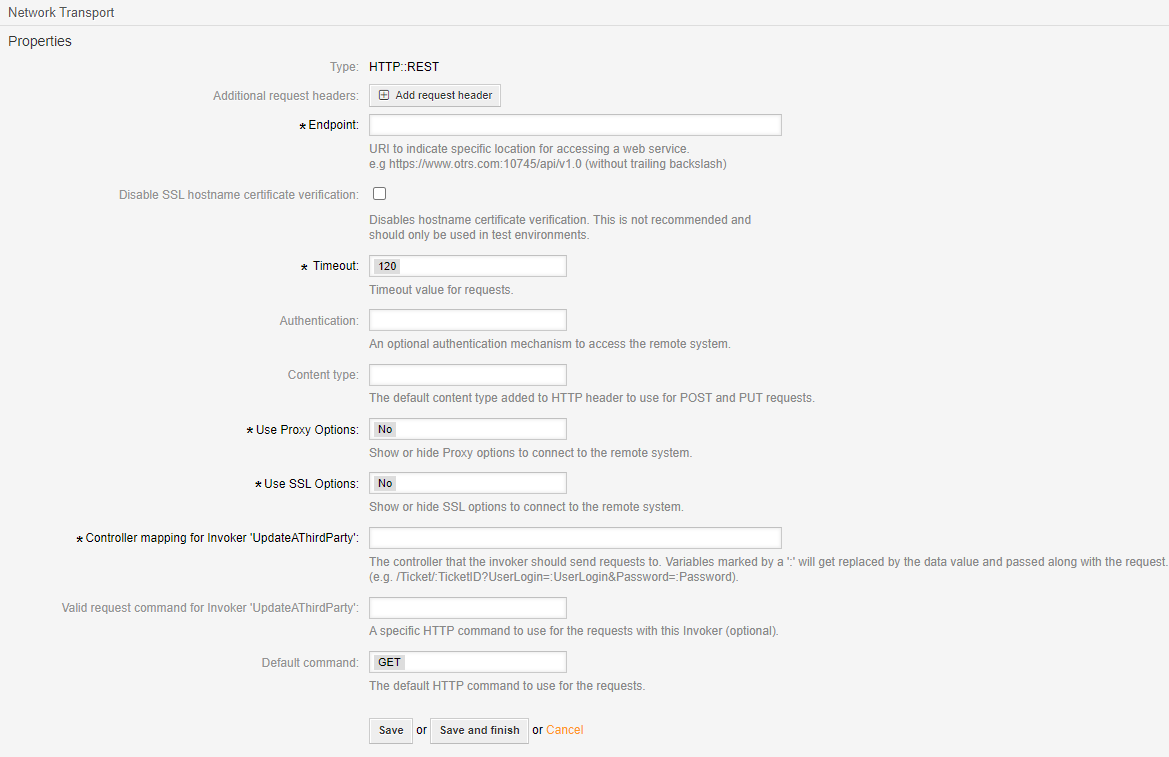
- Endpoint
URI to indicate specific location for accessing a web service.
Note
An example: https://www.otrs.com:10745/api/v1.0 (do not use a trailing backslash)
- Disable SSL hostname certificate verification
Disables hostname certificate verification. This is not recommended and should only be used in test environments.
- Timeout
Timeout value for requests.
- Authentication
An optional authentication mechanism to access the remote system.
- Content type
The default content type added to HTTP header to use for POST and PUT requests.
- Use Proxy Options
Show or hide Proxy options to connect to the remote system.
- Use SSL Options
Show or hide SSL options to connect to the remote system.
- Controller mapping for Invoker ‘UpdateAThirdParty`
The controller that the invoker should send requests to. Variables marked by a ‘:’ will get replaced by the data value and passed along with the request. (e.g. /Ticket/:TicketID?UserLogin=:UserLogin&Password=:Password).
- Valid request command for Invoker ‘UpdateAThirdParty’
A specific HTTP command to use for the requests with this Invoker (optional).
- Default command
The default HTTP command to use for the requests.
SSL Options#
- Client Certificate
The full path and name of the SSL client certificate file (must be in PEM, DER or PKCS#12 format).
Note
An example /opt/otrs/var/certificates/SOAP/certificate.pem
- Client Certificate Key
The full path and name of the SSL client certificate key file (if not already included in certificate file).
Note
An example /opt/otrs/var/certificates/SOAP/key.pem
- Client Certificate Key Password
The password to open the SSL certificate if the key is encrypted.
- Certification Authority (CA) Certificate
The full path and name of the certification authority certificate file that validates SSL certificate.
Note
An example /opt/otrs/var/certificates/SOAP/CA/ca.pem
- Certification Authority (CA) Directory
The full path of the certification authority directory where the CA certificates are stored in the file system.
Note
An example /opt/otrs/var/certificates/SOAP/CA
Authentication Options#
REST#
HTTPBasic Auth
JWT Token
OAuth Token
See also
JSON Web Token (JWT) Authentication Settings#
Supported Algorithms#
RS256
RS384
RS512
- TTL
TTL (time to live) in seconds for the Token. This value will be used to calculate the expiration time which will be available in placeholders ExpirationDateTimestamp and ExpirationDateString.
- Payload
Payload for JWT.
Note
Key Value Pairs
These must be semi-colon separated.
Key1=Value1;Key2=Value2;Key3=Value3
- Available Placeholders
Placeholders can be used in the payload. These must be prefixed with OTRS_JWT.
Note
ExpirationDateTimestam
ExpirationDateString
Additionally if X.509 certificate support is present, you may use the following placeholders:
CertSubject
CertIssuer
CertSerial
CertNotBefore
CertNotAfter
CertEmail
CertVersion
Note
Placeholder usage example: Key1=<OTRS_JWT_ExpirationDateTimestamp>
- Additional header data
Additional header data for JWT.
Note
Key Value Pairs
These must be semi-colon separated.
Key1=Value1;Key2=Value2;Key3=Value3
Note
ExpirationDateTimestam
ExpirationDateString
Additionally if X.509 certificate support is present, you may use the following placeholders:
CertSubject
CertIssuer
CertSerial
CertNotBefore
CertNotAfter
CertEmail
CertVersion
Note
Placeholder usage example: Key1=<OTRS_JWT_ExpirationDateTimestamp>