OAuth2 Token Administration#
OAuth2 Flow Support#
We support the following authorization flows:
Authorization Flow
Client Credentials Flow
Important
The authorization flow is the most common OAuth2 flow. It is used by most providers, including Google and Microsoft. It requires user interaction to authorize the application to access the user’s data.
The client credentials flow is used for server-to-server communication where no user interaction is required.
More background information about OAuth on Wikipedia
Token Usage#
Tokens can currently be used by
PostMaster Mail Accounts
Web Service Invokers
Application Registration#
An application registration is required to access resources via OAuth2. Upon registration, you should receive:
ClientID
Client Secret
Endpoint(s)
Microsoft and IMAP/POP#
Microsoft has switch off basic authentication for IMAP and POP protocols and moved to “Modern Authentication” (which is OAuth 2.0 token based auth) This has many benefits and improvements:
OAuth access tokens have a limited usable lifetime
are specific to the applications and resources they are issued
can’t be re-used
An Example Microsoft App#
In our Blog, we outlined an example setup
Token Settings#
Adding a token will generates a YAML configuration in the database. This file has a specific format depending upon the provider and can be exported, modified, and imported as needed by the configuration or for migration (see below). We include basic formatting templates for the email providers, Google and Microsoft. The configuration is all done comfortably in the web interface, and you may generate as many service tokens as needed for your accounts.
Important
The system setting HttpType must be https for production systems using external services like GMail and Office365.
You can set this using the command-line as follows:
[znuny@host ~]$ bin/znuny.Console.pl Admin::Config::Update --setting-name HttpType --value https
Alternatively, you can search for HttpType in the system configuration and set it there.
Note
After configuration, it may be necessary to edit the endpoints manually, as the service provider can change the requirements at any time.
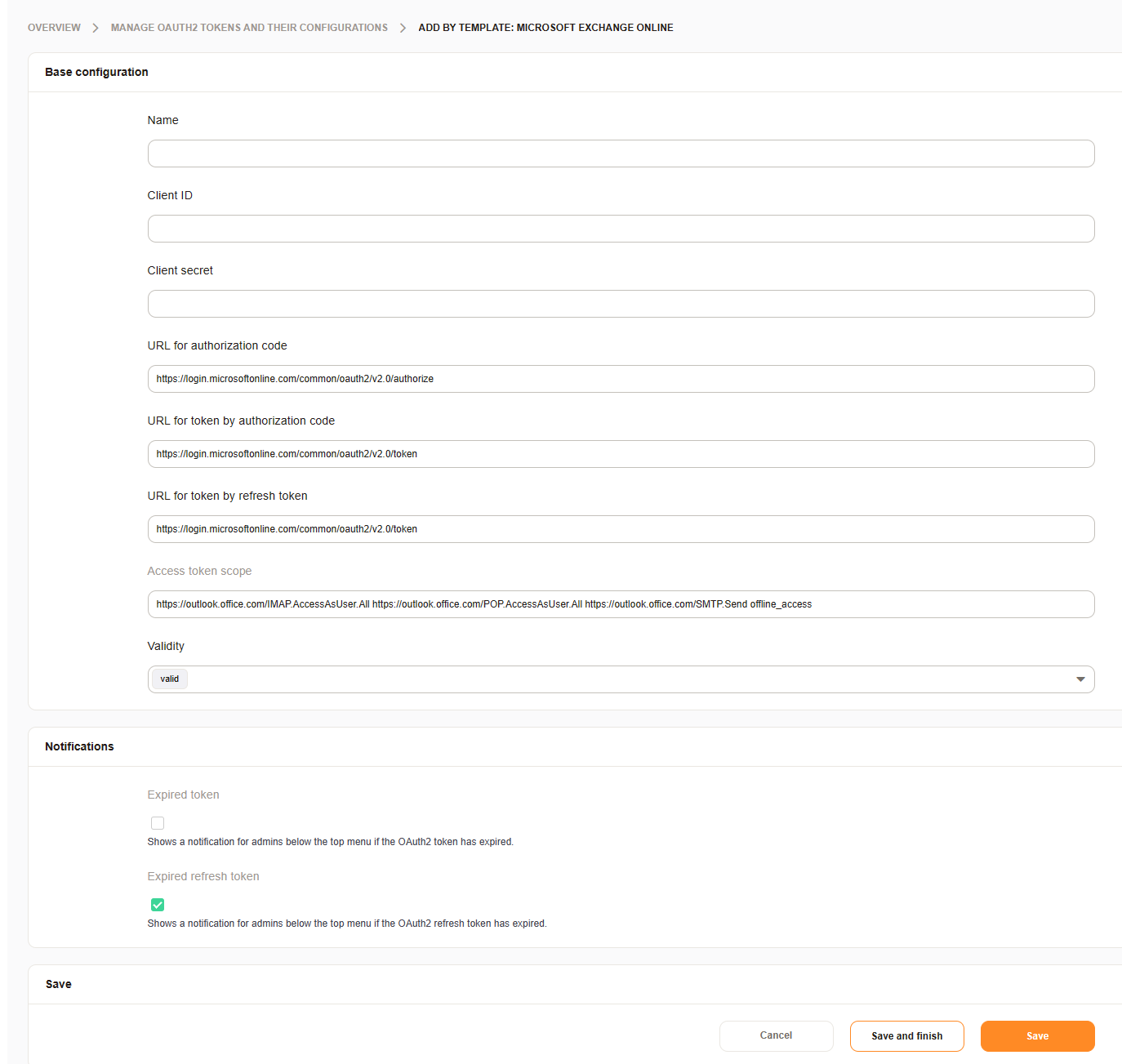
The following fields are needed, depending on the OAuth2 flow:
- Name
A name for the token.
- Client ID
Your client id. (The public identifier.)
- Client secret
Your client secret. (The application’s own password.)
- URL
Enter the endpoints required for authorization, token, and/or token refresh.
- Scope
Add the scope for the token.
- Validity
The validity of the setting.
- Template
Shows the template that was used to create this OAuth2 token configuration.
Types of Notifications to be shown
- Expired token
Shows a notification for admins below the top menu if the OAuth2 token has expired.
- Expired refresh token
Shows a notification for admins below the top menu if the OAuth2 refresh token has expired.
Token Overview#
It the token overview, it is necessary to manually request a new token upon token setup and as required by your service provider. You will receive front-end notifications as configured to inform you when the token or refresh token has expired.
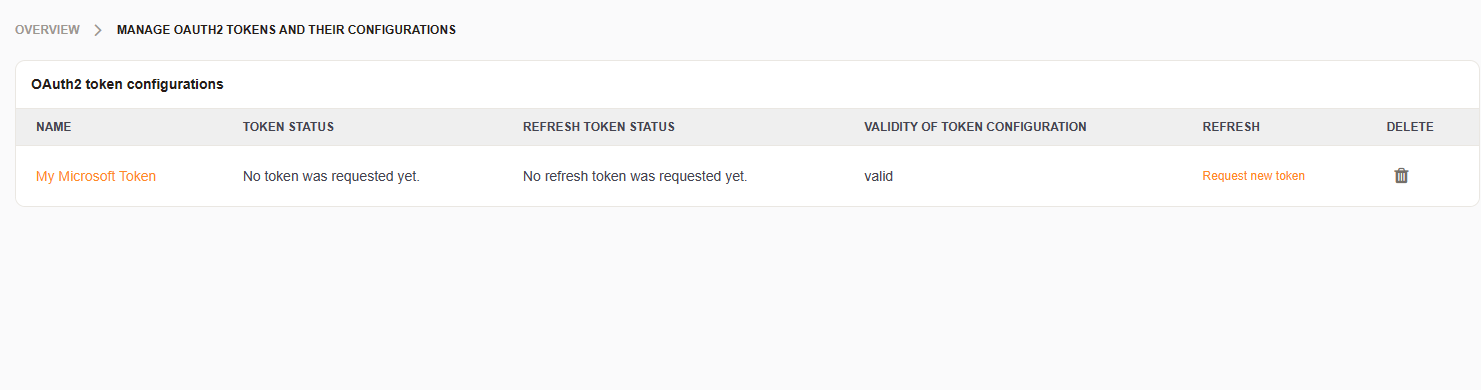
Edit a Token#
Select any token from the overview to edit a token.
Token Notifications#
In the notification area, you receive notifications if a token or refresh token has expired. Clicking the notification will send you to the administration module for renewal. You may then click on refresh to get a new token.

Note
When a refresh token expires, you must generate a new one with your service provider.
Backup and Migration#
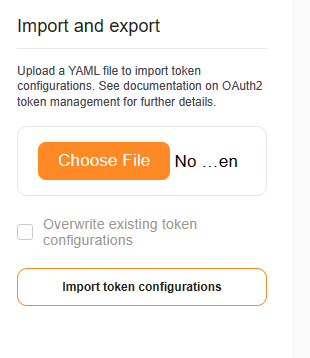
Note
The option to overwrite settings only changes those settings of the same name.
Vendor-Specific Documentation#
Important
- Redirect URI
The redirect_uri for Znuny is built from the system variables in the following manner:
${HttpType}://${FQDN}/${ScriptAlias}/get-oauth2-token-by-authorization-code.pl
i.e.
https://znuny.example.com/otrs/get-oauth2-token-by-authorization-code.pl